Microsoft Excel - VBA

Hello Koalas,
This article contains some VBA code I try in Excel.
Table of Contents
- Print The Workbook Name
- Get the Last Row with xlUp
- Get the Last Column with xlToLeft
- Functions and Subs
- Add Formula to a Cell
- Check Formula before to Run It
- Option Explicit
- Variable Types
- List all sheets in a Workbook
- Copy a Range of Cells
- Find all instances of text in a range with FindNext
- Use of a Dictionary
- Sort a Range
- Sum a Range
- Format a Range
- Create a Sheet
- Delete sheets
Print The Workbook Name
' Print the workbook name
Sub PrintWorkbookName()
Dim wk As Workbook
Set wk = ThisWorkbook
Debug.Print wk.Name
End Sub
Get the Last Row with xlUp
Remark: this code is not the best but it can help in some situation
' Get the last row containing text with xlUp
Sub GetLastRow()
' Get the worksheet call Sheet1 in the current workbook
Dim sh As Worksheet
Set sh = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Sheet1")
' Get last row with text by searching from the bottom of the worksheet in column "A1"
Dim lastRow As Long
lastRow = sh.Cells(sh.Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row
' Print the row number
Debug.Print lastRow
End Sub
Get the Last Column with xlToLeft
Remark: this code is not the best but it can help in some situation
Sub GetLastColumn()
' Get the worksheet call Sheet1 in the current workbook
Dim sh As Worksheet
Set sh = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Sheet1")
' Get last column with text by searching from the right of the worksheet in first row
Dim lastColumn As Long
lastColumn = sh.Cells(1, sh.Columns.Count).End(xlToLeft).Column
Debug.Print lastColumn
End Sub
Functions and Subs
It has 2 types of procedures in VBA:
- Functions
- Subs
The major difference between both is that functions return a value and subs don't.
To return a value from a function your assign the name of the function.
Example:
Function Calc(a as Long, b as Long) As Long
' This will return the result from this function
Calc = (a + b)*10
End Function
You have to use a Sub or an object to run the function.
Sub CallFunction()
Dim result As Long
result = Calc(3, 4)
Debug.Print result
End Sub
Another example:
Function GetWorkbookObject() As Workbook
Set GetWorkbookObject = ThisWorkbook
End Function
Sub CallGetWorkbookObject()
Dim wk As Workbook
Set wk = GetWorkbookObject
Debug.Print wk.Name
End Sub
Add Formula to a Cell
Add a formula to a cell.
Sub AddFormulaToCell()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = Worksheets("Sheet1")
ws.Range("A1").Value = 3
ws.Range("A2").Value = 5
ws.Range("A3").Formula = "=sum(A1:A2)"
End Sub
Check Formula before to Run It
This code does a basic check before to run the formula.
Sub CheckFormula()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = Worksheets("Sheet1")
Dim myFormula As String
myFormula = "=Sum(C0:C2)"
ws.Range("C1").Value = 5
ws.Range("C2").Value = 6
If IsError(Evaluate(myFormula)) Then
Debug.Print "An error occured with the formula: " & myFormula
Else
Debug.Print "The formula " & myFormula; " is valid."
End If
End Sub
Option Explicit
When "Option Explicit" is placed at the top of a module it means a variable must be declared before you can use it.
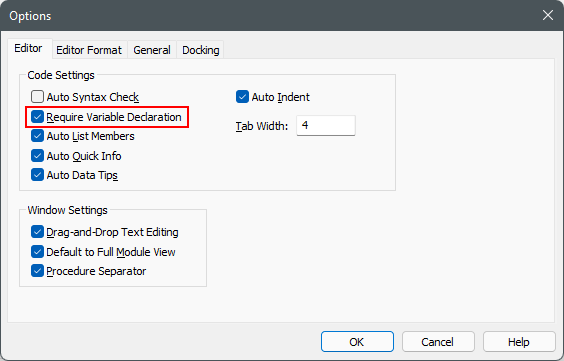
Variable Types
Here are the 4 most common variable types:
| What | VBA Type |
|---|---|
| Text | String |
| Integer | Long |
| Decimal | Double |
| Currency | Currency (4 decimal places only) |
| Date | Date |
List all sheets in a Workbook
You can access all worksheets inside your workbook by using a "For Each" loop.
"For Each" loop:
' Shows all sheets in the Workbook
Sub AccessAllWorksheets()
Dim wb As Workbook
Set wb = ThisWorkbook
Dim sheet As Worksheet
For Each sheet In wb.Worksheets()
Debug.Print sheet.Name
Next
End Sub
"For" loop:
Sub AccessAllWorksheetsWithForLoop()
Dim wb As Workbook
Set wb = ThisWorkbook
Dim i As Long
For i = 1 To wb.Worksheets.Count
Debug.Print wb.Worksheets(i).Name
Next
Debug.Print "--- Reverse order ---"
For i = wb.Worksheets.Count To 1 Step -1
Debug.Print wb.Worksheets(i).Name
Next
End Sub
Copy a Range of Cells
Two ways of copying a range of cells.
' Copy a range of cells
Sub CopyRangeCells()
Dim wb As Workbook
Set wb = ThisWorkbook
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = Worksheets("Sheet1")
' Version 1
ws.Range("A1:A2").Copy
ws.Range("A6").PasteSpecial Paste:=xlPasteValues
' Version 2
Range("C1:C2").Copy Destination:=Range("C6")
End Sub
Find all instances of text in a range with FindNext
Search for all instances of a specific text with the method FindNext.
Sub FindTextInRangeCells()
Dim wb As Workbook
Set wb = ThisWorkbook
Dim rg As Range
Set rg = wb.Worksheets("Sheet1").Range("A1:C7").Find("5", LookIn:=xlValues)
If rg Is Nothing Then
Debug.Print "Value not found."
Exit Sub
End If
Dim firstResult As String
firstResult = rg.Address
Do
Debug.Print "Address: " & rg.Address, "Row: " & rg.Row, "Column: " & rg.Column
'Find next item
Set rg = wb.Worksheets("Sheet1").Range("A1:C7").FindNext(rg)
Loop Until rg Is Nothing Or firstResult = rg.Address
End Sub
Use of a Dictionary
Use of a dictionary.
' Use of Dictionary
Sub PlayWithDictionary()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = Worksheets("Sheet1")
' Declare and create a dictionary
Dim dict As Object
Set dict = CreateObject("Scripting.Dictionary")
' Add item - error if already exists
dict.Add "Apples", 10
' Silently add items - updates if already exists
dict("Apples") = 20
dict("Bananas") = 12
' Access items stored at Key - ex: print 20
Debug.Print "Total of Apples is: " & dict("Apples")
If dict.Exists("Apples") Then
Debug.Print "Apples has been found. Value is: " & dict("Apples")
End If
' Loop through all items
Dim Key As Variant
Debug.Print "Print all items in the Dictionary"
For Each Key In dict.Keys
Debug.Print Key, dict(Key)
Next
' Remove all items
dict.RemoveAll
End Sub
Sort a Range
Create a range and then sort it by using a specific column as sort filter.
Sub SortARange()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = Worksheets("Sheet1")
Dim rg As Range
Dim rgSortBy As Range
ws.Range("F1").Value = "A"
ws.Range("F2").Value = "D"
ws.Range("F3").Value = "B"
ws.Range("F4").Value = "C"
ws.Range("F5").Value = "E"
ws.Range("G1").Value = "Toto"
ws.Range("G2").Value = "Titi"
ws.Range("G3").Value = "Tutu"
ws.Range("G4").Value = "Tata"
ws.Range("G5").Value = "Tete"
' Range to sort
Set rg = Range("F1:G5")
' Column to sort by
Set rgSortBy = Range("F1:F5")
' Sort the items
rg.Sort rgSortBy, xlAscending
End Sub
Sum a Range
Sum a range of values. A1 = 3 ; A2 = 5 ; A3 = 8.
Sub SumARange()
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = Worksheets("Sheet1")
Dim rg As Range
Set rg = Range("A1:A3")
Debug.Print "Sum of a Range is:"; WorksheetFunction.Sum(rg)
End Sub
Format a Range
Format some cells with basic parameters.
Sub FormatRange()
Dim i As Long
Dim cellNumber As Long
cellNumber = 10
For i = 1 To 10
Range("A" & cellNumber).Value = i
cellNumber = cellNumber + 1
Next
With Range("A10:A19")
' Set Font Attributes
.Font.Bold = True
.Font.Size = 10
.Font.Color = rgbRed
.HorizontalAlignment = xlCenter
' Set Fill Color
.Interior.Color = rgbLightBlue
' Set Borders
.Borders.LineStyle = xlDouble
.Borders.Color = rgbGreen
End With
'Range("A10:A20").Clear
End Sub
Create a Sheet
Create a sheet.
Sub CreateSheet()
Dim sh As Worksheet
Set sh = Worksheets.Add(After:=Worksheets("Sheet1"))
sh.Name = "NewSheet"
End Sub
Delete sheets
Delete all sheets except the one with the name "Sheet1".
Sub DeleteSheets() Dim sh As Worksheet Set sh = Worksheets.Add(After:=Worksheets("Sheet1")) Application.DisplayAlerts = False For Each sh In Worksheets If sh.Name <> "Sheet1" Then sh.Delete End If Next Application.DisplayAlerts = True End Sub
